VMware Explore US 2022 – Summary of Day 1 Announcements
VMworld is now VMware Explore and is currently happening in San Francisco! This is a consolidated of the announcements from day 1 (August 30th, 2022).
VMware Introduces vSphere 8, vSAN 8 and VMware Cloud Foundation+
VMware today introduced VMware vSphere 8 and VMware vSAN 8—major new releases of VMware’s compute and storage solutions.
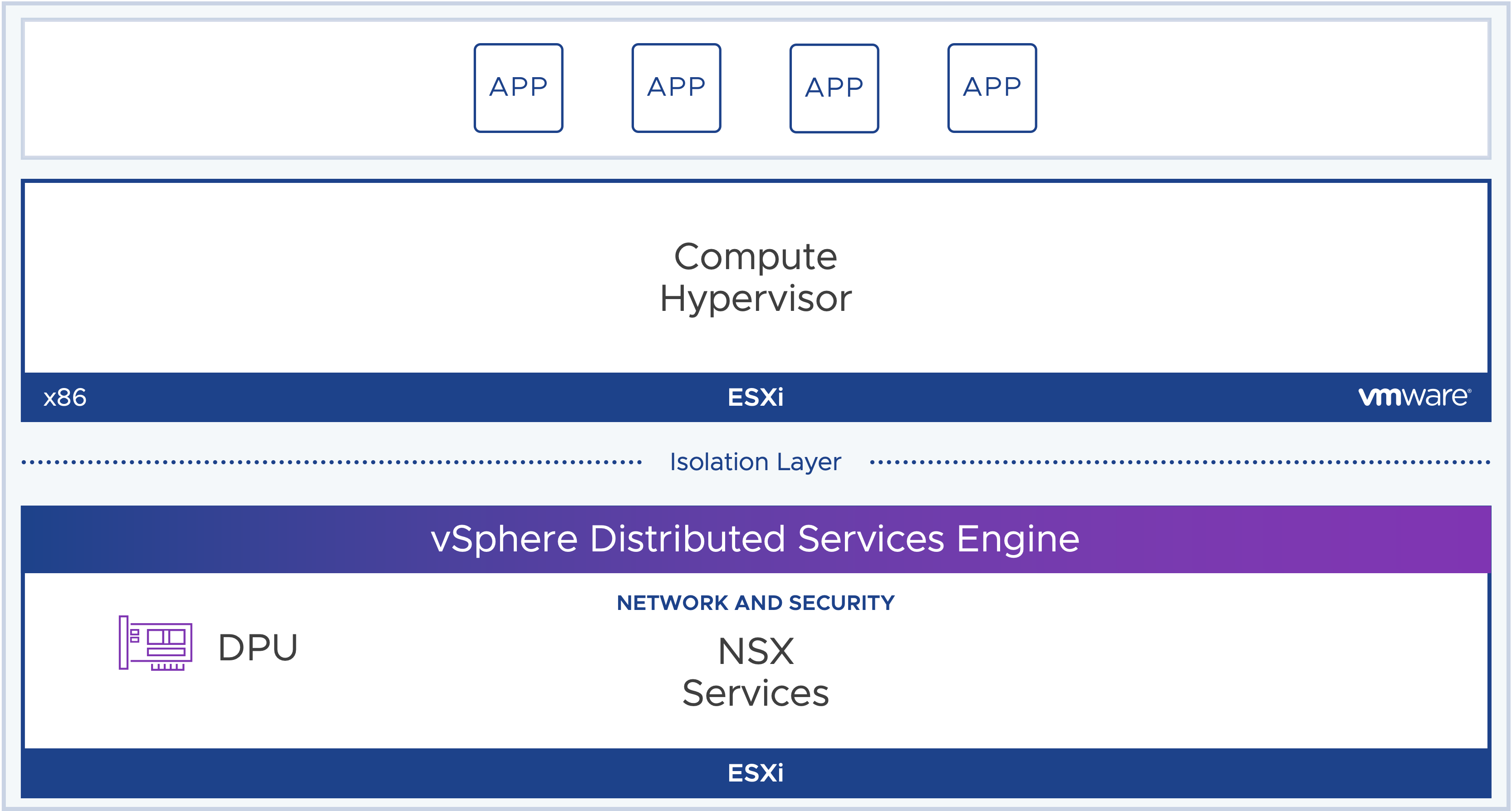
vSphere 8 – vSphere 8 introduces vSphere on DPUs, previously known as Project Monterey. In close collaboration with technology partners AMD, Intel and NVIDIA as well as OEM system partners Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Lenovo, vSphere on DPUs will unlock hardware innovation helping customers meet the throughput and latency needs of modern distributed workloads. vSphere will enable this by offloading and accelerating network and security infrastructure functions onto DPUs from CPUs.
vSphere 8 will dramatically accelerate AI and machine learning applications by doubling the virtual GPU devices per VM, delivering a 4x increase of passthrough devices, and supporting vendor device groups which enable binding of high-speed networking devices and the GPU.
vSAN 8: vSAN 8 introduces breakthrough performance and hyper-efficiency. Built from the ground up, the new vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA) will enhance the performance, storage efficiency, data protection and management of vSAN running on the latest generation storage devices. vSAN 8 will provide customers with a future ready infrastructure that supports modern TLC storage devices and delivers up to a 4x performance boost.

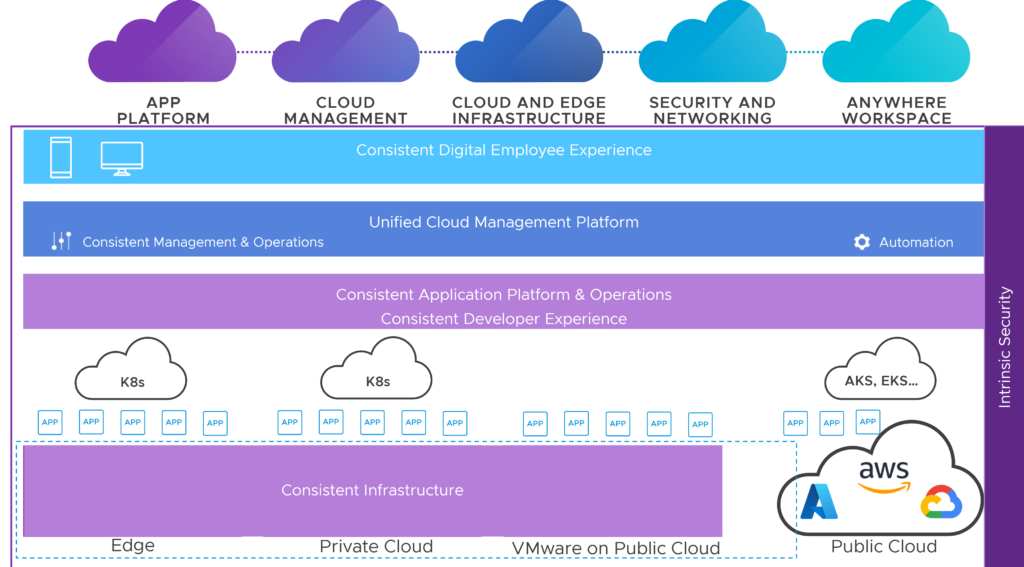
VMware Cloud Foundation+ – VMware introduces a new cloud-connected architecture for managing and operating full stack HCI in data centers. Built on vSphere+ and vSAN+, VMware Cloud Foundation+ will add a new cloud-connected architecture for managing and operating full-stack HCI in our data center or co-location facility.

VMware Cloud Foundation+ will deliver new admin, developer and hybrid cloud services through a simplified subscription model and keyless entitlement. VMware Cloud Foundation 4.5 will enable VMware Cloud Foundation+ by adding vSphere+ and vSAN+, plus a cloud gateway that provides access to the VMware Cloud Console as part of the full stack architecture.
VMware Cloud for Hyperscalers
VMC on AWS – Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) I4i instances for I/O-intensive Workloads: Powered by 3rd generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors (Ice Lake), Amazon EC2 instances help deliver better workload support and delivery, lower TCO, and increased scalability and application performance. Compared to I3, the I4i instances provide nearly twice the number of physical cores, twice the memory, three times the storage capacity, and three times the network bandwidth.
Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP Integration Availability – as a native AWS cloud storage service that is certified as a supplemental datastore for VMware Cloud on AWS, FSx for ONTAP offers fully managed shared storage built on the familiar NetApp ONTAP file system trusted by VMware customers running on premises today. Customers can now use FSx for ONTAP as a simple and elastic datastore for VMware Cloud on AWS, enabling them to scale storage up or down independently from compute while paying only for the resources they need.

VMware Cloud Flex Storage Availability – A new VMware-managed and natively integrated cloud storage and data management solution that offers supplemental datastore-level access for VMware Cloud on AWS. With just a few clicks in the VMware Cloud Console, customers can scale their storage environment without adding hosts, and elastically adjust storage capacity up or down as needed for every application. Customers also benefit from a simple, pay-as-you-consume pricing model. Together with VMware vSAN, VMware Cloud Flex Storage offers flexibility and customer value in terms of resilience, performance, scale, and cost in the cloud.

VMware Cloud Flex Compute – “Preview” of a new cloud compute model that will help customers get started faster with VMware Cloud on AWS. With this new model, VMware introduces a “resource-defined” cloud compute model in place of “hardware-defined” compute instance model which will provide customers higher flexibility, elasticity, and speed to better meet cost and performance requirements of enterprise applications. It will help customers get started faster with VMware Cloud on AWS by using smaller consumable units.

Azure VMware Solution – Customers will be able to purchase Azure VMware Solution as part of VMware Cloud Universal, a flexible purchasing and consumption program for executing multi-cloud and digital transformation strategies. VMware Cloud Director Service for Azure VMware Solution is also now available in Public Preview.
Google Cloud VMware Engine – VMware announced VMware Tanzu Standard edition on Google Cloud VMware Engine to help simplify Kubernetes adoption and management.
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution – New features and capabilities with VMware Tanzu Standard Edition and introduced support for single host SDDCs for non-production workloads.
VMware Cloud Management – VMware Aria
VMware unveiled a multi-cloud management portfolio called VMware Aria, which provides a set of end-to-end solutions for managing the cost, performance, configuration, and delivery of infrastructure and cloud native applications.
VMware Aria is a new brand for the vRealize components, Tanzu Observability by Wavefront and CloudHealth unified under one umbrella, one name.
The VMware products and services within the VMware Aria portfolio are:
- VMware Aria Automation (formerly, vRealize Automation)
- VMware Aria Operations (formerly, vRealize Operations)
- VMware Aria Operations for Networks (formerly, vRealize Network Insight)
- VMware Aria Operations for Logs (formerly, vRealize Log Insight)
- VMware Aria Operations for Secure Clouds (formerly, CloudHealth Secure State)
- VMware Aria Cost powered by CloudHealth (formerly, CloudHealth)
- VMware Aria Operations for Applications (formerly VMware Tanzu Observability)
- VMware Skyline

VMware Aria is anchored by VMware Aria Hub (formerly known as Project Ensemble), which provides centralized views and controls to manage the entire multi-cloud environment, and leverages VMware Aria Graph to provide a common definition of applications, resources, roles, and accounts.

VMware Aria Graph provides a single source of truth that is updated in near-real time. Other solutions on the market were designed in a slower moving era, primarily for change management processes and asset tracking. By contrast, VMware Aria Graph is designed expressly for cloud-native operations.
VMware Aria provides features and functions that span management disciplines and clouds to deliver unique value for multi-cloud governance, cross-cloud migration, and actionable business insights. In addition, there are three new end-to-end management services built on top of VMware Aria Hub and VMware Aria Graph:
- VMware Aria Guardrails – Automate enforcement of cloud guardrails for networking, security, cost, performance, and configuration at scale for multi-cloud environments with an everything-as-code approach
- VMware Aria Migration – Accelerate and simplify the multi-cloud migration journey by automating assessment, planning, and execution in conjunction with VMware HCX
- VMware Aria Business Insights – Discern relevant business insights from full-stack event correlation leveraging AI/ML analytics
Networking and Security
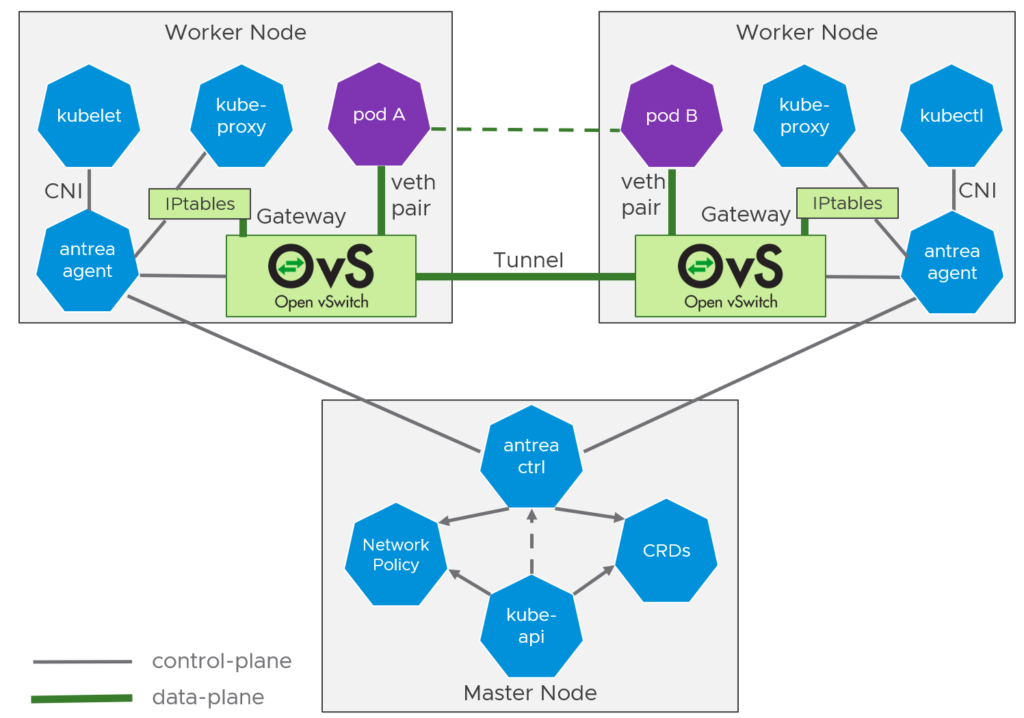
Project Northstar – Project Northstar is a SaaS-based network and security offering that will empower NSX customers with a set of on-demand multi-cloud networking and security services, end-to-end visibility, and controls. Customers will be able to use a centralized cloud console to gain instant access to networking and security services, such as network and security policy controls, Network Detection and Response (NDR), NSX Intelligence, Advanced Load Balancing (ALB), Web Application Firewall (WAF), and HCX. It will support both private cloud and VMware Cloud deployments running on public clouds and enable enterprises to build flexible network infrastructure that they can spin up and down in minutes.

DPU-based Acceleration for NSX – Formerly known as Project Monterey, VMware announced that starting with NSX 4.0 and vSphere 8.0, customers can leverage DPU-based acceleration using SmartNICs. Offloading NSX services to the DPU can accelerate networking and security functions without impacting the host CPUs, addressing the needs of modern applications and other network-intensive and latency-sensitive applications.

Project Trinidad – Available as tech preview, Project Trinidad extends VMware’s API security and analytics by deploying sensors on Kubernetes clusters and uses machine learning with business logic inference to detect anomalous behavior in east-west traffic between microservices.
Project Watch – VMware unveiled Project Watch, a new approach to multi-cloud networking and security that will provide advanced app-to-app policy controls to help with continuous risk and compliance assessment. In technology preview, Project Watch will help network security and compliance teams to continuously observe, assess, and dynamically mitigate risk and compliance problems in composite multi-cloud applications.

Additionally, VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer adds new bot management capabilities to help enterprises address threats quickly and efficiently, providing enhanced multi-layer application protection with existing Web Application Firewall, DDoS protection, and API security.
Edge
VMware Edge Compute Stack 2.0 – VMware announced the VMware Edge Compute Stack v1.0 last year and is now adding more features and functionalities optimized for different use cases at the enterprise edge – shipped with vSphere 8 and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid 2.0. VMware, for the first time, will introduce initial support for non-x86 processor-based specialized small form factor edge platforms to simultaneously run IT/OT workloads and workflows on a single stack.
 VMware Private Mobile Network (Beta) – Delivered by service providers, this new managed service offering provides enterprises with private 4G/5G mobile connectivity in support of edge-native applications. VMware will empower partners with a single PMN orchestrator to operate multi-tenant private 4G/5G networks with an enterprise-grade solution.
VMware Private Mobile Network (Beta) – Delivered by service providers, this new managed service offering provides enterprises with private 4G/5G mobile connectivity in support of edge-native applications. VMware will empower partners with a single PMN orchestrator to operate multi-tenant private 4G/5G networks with an enterprise-grade solution.
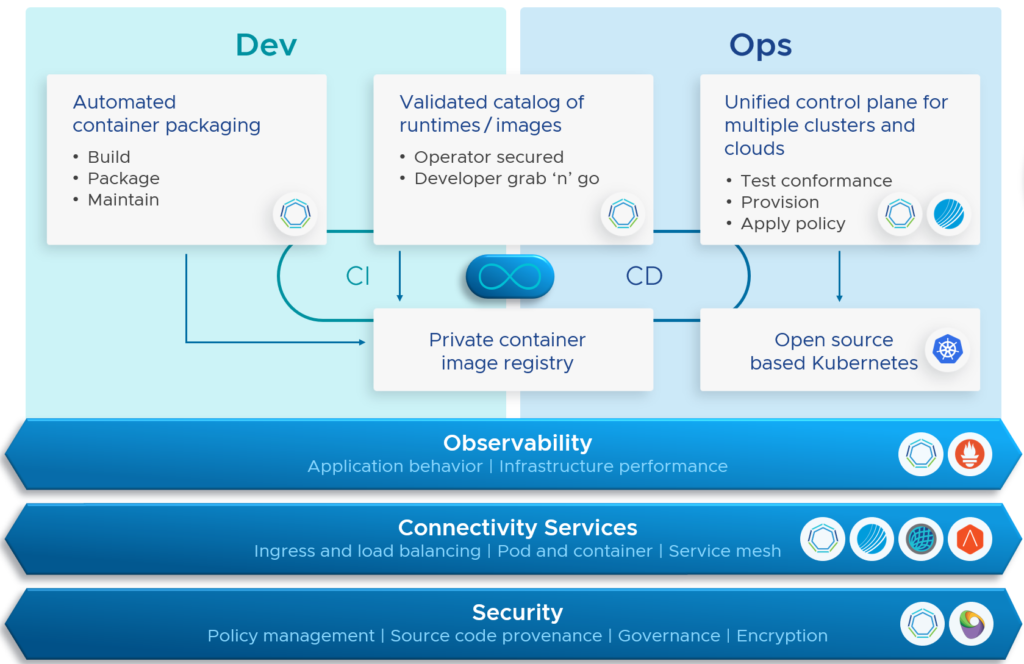
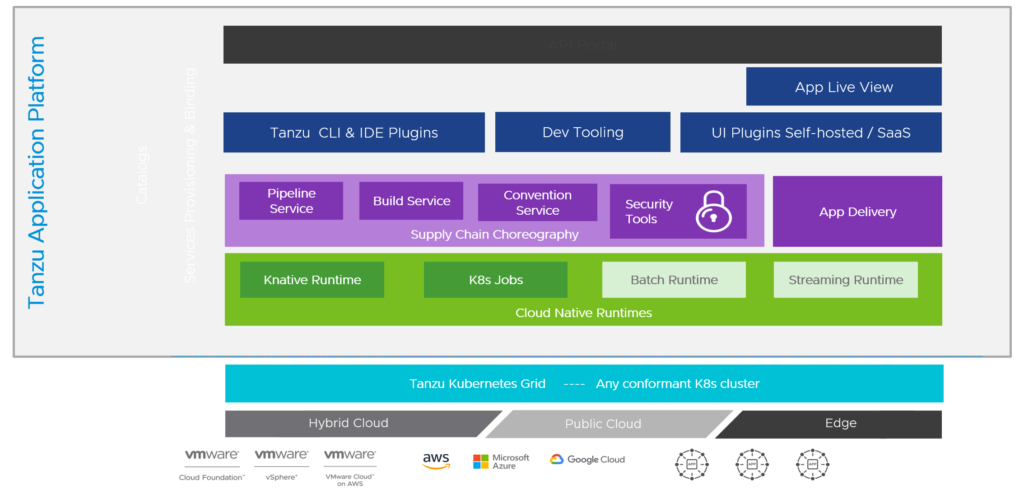
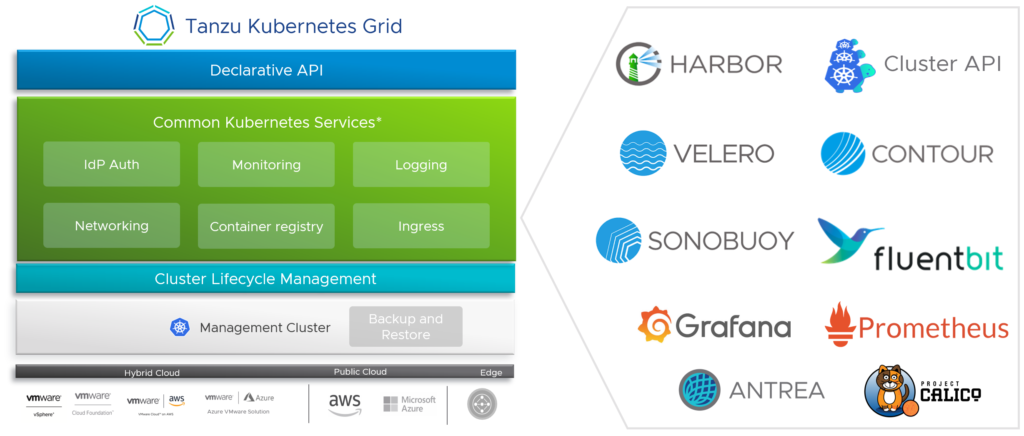
Modern Applications (VMware Tanzu)
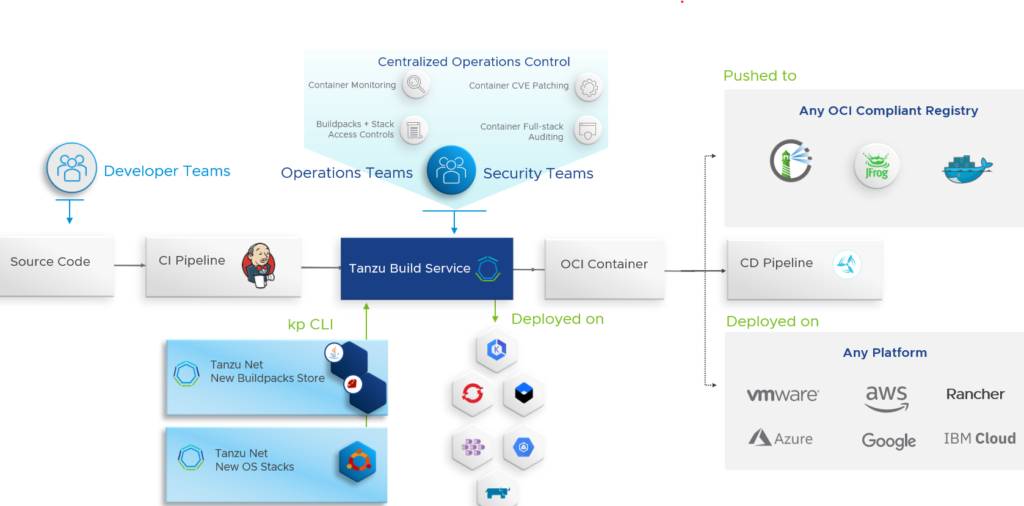
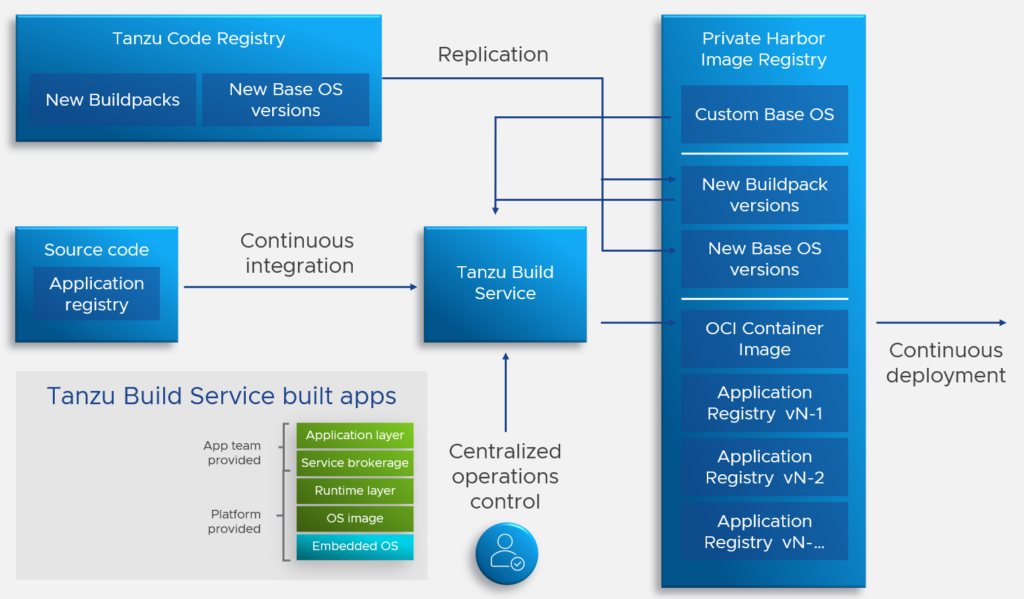
Tanzu Application Platform – VMware pre-announced new Tanzu Application Platform (TAP) 1.3 capabilities like the availability on RedHat OpenShift or the support for air-gapped installations for regulated and disconnected environments.
Tanzu Mission Control – Finally, VMware announced the preview for lifecycle management of Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) clusters, which enables direct provisioning and management of EKS clusters, which is awesome! I suppose we can expect the support for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) also coming very soon.
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid – With the release of TKG 2.0, VMware now includes a unified experience for applications running on any cloud. In the near future, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid 2.0 should support both Supervisor-based and VM-based management cluster models. On vSphere 8, both Supervisor-based and VM-based models will be supported, and VM-based management clusters will continue to be available on previous versions of vSphere and public clouds. This means in other words, that VMware continues with their “TKGS” and “TKGm” flavors.
Tanzu Service Mesh – Also pre-announced, VMware is adding several enterprise and application resiliency capabilities into Tanzu Service Mesh:
- Support for customer-owned enterprise certificate authority through integration with Venafi
- Improved security with enterprise-approved container image registries, data services support, external services support
- and a global SLO dashboard that allows developers and site-reliability engineers to view all managed service SLOs, helping with capacity planning, troubleshooting, and understanding the health of their applications.
Read more about all the Tanzu announcements here.
Anywhere Workspace
VMware unveiled how it is advancing self-configuring, self-healing and self-securing outcomes across four key technology areas that are delivered by the Anywhere Workspace platform:
- VDI and DaaS
- Digital Employee Experience
- Unified Endpoint Management
- Security
VMware is introducing a next generation of VMware Horizon Cloud that will enable multi-cloud agility and flexibility. This new release represents a major update to Horizon Cloud on Microsoft Azure that can dramatically simplify the infrastructure that needs to be deployed inside customer environments, reducing infrastructure costs in some cases by over 70% while increasing scalability and reliability of VMware’s DaaS platform.

Workspace ONE UEM’s Freestyle Orchestrator will be expanding to include support for mobile devices.
Workspace ONE support for Windows OS multi-user mode is now available in Tech Preview for Azure Active Directory-based deployments; and it will soon be extended to Active Directory-based deployments.
VMware also announced the coming tech preview of Workspace ONE Cloud Marketplace, which will feature dashboards, widgets, reports, Freestyle Orchestrator workflows, and other resources that can be imported to help customers adopt additional solutions.
Horizon Managed Desktop – I am very excited about this announcement, because it will provide a managed service offering that takes care of lifecycle services, support, and more, on top of a customer-provided infrastructure. This will help customers that don’t have in-house experts get to value with VDI faster.
Availability
VMware Cloud Foundation+, VMware vSphere 8, VMware vSAN 8 and VMware Edge Compute Stack 2.0 are all expected to be available by October 28, 2022 (the close of VMware’s Q3 FY23). VMware Private Mobile Network is expected to be available in beta in VMware’s Q3 FY23.
Closing Comment
Not bad for the first day, right? Stay tuned for more exciting VMware Explore announcements!